 中国和印度哪个国家的外汇储备量更高?一个国家拥有大量外汇储备是否有益?
中国和印度哪个国家的外汇储备量更高?一个国家拥有大量外汇储备是否有益?
Which country has a higher amount of foreign exchange reserves, China or India? Is it beneficial for a country to have a large amount of foreign exchange reserves?
译文简介
网友:截至2023年末,中国外汇储备约3.2万亿美元,印度外汇储备6000亿美元。因此从绝对值来看,中国的外汇储备是印度的五倍多。大多数情况下,一个国家拥有大量的外汇储备是好事,但这个问题也不是那么绝对......
正文翻译
Profile photo for Aya Shawn
Aya Shawn
Living in Singapore, professional investor
As of the end of 2023, China's foreign exchange reserves were approximately US$3.2 trillion, and India's foreign exchange reserves were US$600 billion.
So in absolute terms, China's foreign exchange reserves are more than five times that of India.
In most cases, it is good for a country to have large foreign exchange reserves, but this issue is not so absolute.
First of all, we must understand why a country needs foreign exchange reserves?
When a country needs to purchase foreign goods, services and technology. There are two options
1. Use your own currency to buy (such as Indian rupee, Chinese RMB)
The prerequisite is that the seller recognizes the currency of the country
2. Use international currencies to buy (such as US dollars, euros)
If the seller does not recognize the currency of the country, you can only use international currency to buy
截至2023年末,中国外汇储备约3.2万亿美元,印度外汇储备6000亿美元。
因此从绝对值来看,中国的外汇储备是印度的五倍多。
大多数情况下,一个国家拥有大量的外汇储备是好事,但这个问题也不是那么绝对。
首先我们要明白一个国家为什么需要外汇储备?
当一个国家需要购买外国商品、服务和技术时,有两种选择
1. 使用本国货币购买(如印度卢比、中国人民币)
前提是卖家认可该国货币
2.使用国际货币购买(如美元、欧元)
如果卖家不识别该国货币,则只能使用国际货币购买
原创翻译:龙腾网 https://www.ltaaa.cn 转载请注明出处
Aya Shawn
Living in Singapore, professional investor
As of the end of 2023, China's foreign exchange reserves were approximately US$3.2 trillion, and India's foreign exchange reserves were US$600 billion.
So in absolute terms, China's foreign exchange reserves are more than five times that of India.
In most cases, it is good for a country to have large foreign exchange reserves, but this issue is not so absolute.
First of all, we must understand why a country needs foreign exchange reserves?
When a country needs to purchase foreign goods, services and technology. There are two options
1. Use your own currency to buy (such as Indian rupee, Chinese RMB)
The prerequisite is that the seller recognizes the currency of the country
2. Use international currencies to buy (such as US dollars, euros)
If the seller does not recognize the currency of the country, you can only use international currency to buy
截至2023年末,中国外汇储备约3.2万亿美元,印度外汇储备6000亿美元。
因此从绝对值来看,中国的外汇储备是印度的五倍多。
大多数情况下,一个国家拥有大量的外汇储备是好事,但这个问题也不是那么绝对。
首先我们要明白一个国家为什么需要外汇储备?
当一个国家需要购买外国商品、服务和技术时,有两种选择
1. 使用本国货币购买(如印度卢比、中国人民币)
前提是卖家认可该国货币
2.使用国际货币购买(如美元、欧元)
如果卖家不识别该国货币,则只能使用国际货币购买
原创翻译:龙腾网 https://www.ltaaa.cn 转载请注明出处
2020 data
For countries with weak economic strength, the recognition of their national currency in the world is limited. Most sellers won't accept it, which means you have to use international currency to buy. If there is a lack of sufficient international currency, then a country's international trade will be hindered, some necessities provided by foreign countries will be scarce, and parts and materials imported from foreign countries will be exhausted. This often means chaos in the national economy and the cessation of industrial production.
Therefore, for most countries in the world, foreign exchange reserves are very important. China implemented increasing foreign exchange reserves as a national strategic goal 20 years ago. This has gradually made China the country with the largest foreign exchange reserves in the world.
However, when China's economy developed to a certain level, they discovered that excessive foreign exchange reserves were not the best choice. Therefore, starting from 2014, China began to reduce its foreign exchange reserves in a planned way.
Let's take a look at the two pictures below, which show the changes in China's and India's foreign exchange reserves over the past 10 years.
对于经济实力较弱的国家,其本国货币在国际上的认可度有限,大部分卖家不接受,就只能用国际货币来买。如果缺乏足够的国际货币,那么一个国家的国际贸易就会受到阻碍,一些外国提供的必需品就会短缺,从外国进口的零部件和材料就会枯竭,这往往意味着国家经济的混乱,工业生产的停止。
因此,对于世界上大多数国家来说,外汇储备是非常重要的,中国在20年前就把增加外汇储备作为国家战略目标,这让中国逐渐成为世界上外汇储备最多的国家。
但当中国经济发展到一定程度的时候,发现过多的外汇储备并不是最好的选择,因此从2014年开始,中国开始有计划地减少外汇储备。
我们来看看下面两张图,显示的是过去10年中国和印度外汇储备的变化。
For countries with weak economic strength, the recognition of their national currency in the world is limited. Most sellers won't accept it, which means you have to use international currency to buy. If there is a lack of sufficient international currency, then a country's international trade will be hindered, some necessities provided by foreign countries will be scarce, and parts and materials imported from foreign countries will be exhausted. This often means chaos in the national economy and the cessation of industrial production.
Therefore, for most countries in the world, foreign exchange reserves are very important. China implemented increasing foreign exchange reserves as a national strategic goal 20 years ago. This has gradually made China the country with the largest foreign exchange reserves in the world.
However, when China's economy developed to a certain level, they discovered that excessive foreign exchange reserves were not the best choice. Therefore, starting from 2014, China began to reduce its foreign exchange reserves in a planned way.
Let's take a look at the two pictures below, which show the changes in China's and India's foreign exchange reserves over the past 10 years.
对于经济实力较弱的国家,其本国货币在国际上的认可度有限,大部分卖家不接受,就只能用国际货币来买。如果缺乏足够的国际货币,那么一个国家的国际贸易就会受到阻碍,一些外国提供的必需品就会短缺,从外国进口的零部件和材料就会枯竭,这往往意味着国家经济的混乱,工业生产的停止。
因此,对于世界上大多数国家来说,外汇储备是非常重要的,中国在20年前就把增加外汇储备作为国家战略目标,这让中国逐渐成为世界上外汇储备最多的国家。
但当中国经济发展到一定程度的时候,发现过多的外汇储备并不是最好的选择,因此从2014年开始,中国开始有计划地减少外汇储备。
我们来看看下面两张图,显示的是过去10年中国和印度外汇储备的变化。
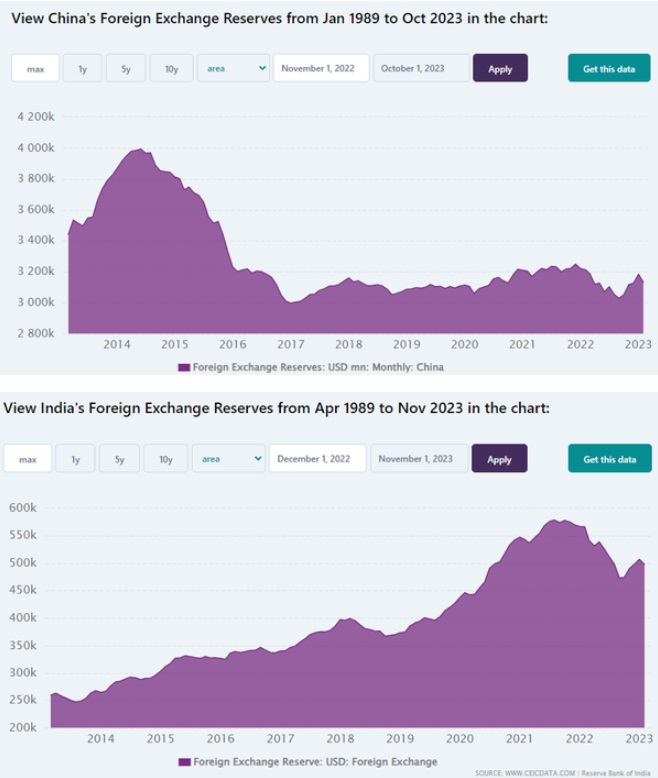
We can see that India is still on the trend of increasing reserves. In the three years of the pandemic, India has spent a lot of foreign exchange, causing some media to start reporting "India's foreign exchange reserves crisis."
Foreign exchange is very important to India. Whether it is importing oil, natural gas, pharmaceutical raw materials, semiconductors and machine parts, a large amount of foreign exchange is required. The repayment of some international loans also requires the use of foreign exchange. If India's foreign exchange reserves fall to dangerous levels, global financial institutions will downgrade India's credit rating. They will think: India has lost its ability to pay and its credit.
The fundamental reason here is simple. The problem faced by India is the same as that of most countries: the domestic currency (rupee) does not have enough international credit. After foreign businesses and governments receive rupees, there is not much they can buy from India. This means that large rupees are worthless paper to many countries. Russia's decision to stop accepting rupee payments is a case in point.
China has already passed this stage, and they are actually planning to reduce their foreign exchange reserves. Starting in 2015, they pushed down reserves. Their efforts even encountered challenges after the pandemic began, with excessive exports allowing foreign exchange reserves to rise again. Their banks even started lending large sums of foreign currency to other countries: there was just too much.
Why does China want to reduce its foreign exchange reserves? Because for China, excessive foreign exchange reserves are no longer necessary.
我们看到,印度依然处于增加储备的趋势,大流行三年来,印度花费了大量外汇,导致一些媒体开始报道“印度外汇储备危机”。
外汇对印度来说非常重要,无论是进口石油、天然气、医药原料、半导体、机器零部件,都需要大量外汇,偿还一些国际贷款也需要用到外汇。如果印度外汇储备跌到危险的水平,全球金融机构就会下调印度的信用评级,他们会认为:印度已经丧失了支付能力,丧失了信用。
根本原因很简单。印度面临的问题与大多数国家一样:本国货币(卢比)没有足够的国际信用。外国企业和政府收到卢比后,可以从印度购买的东西并不多。这意味着大额卢比对许多国家来说都是一文不值的纸。俄罗斯决定停止接受卢比支付就是一个例子。
中国已经过了这一阶段,他们实际上正在计划减少外汇储备。从2015年开始,他们就压低了储备。他们的努力甚至在大流行开始后也遇到了挑战,出口过多使得外汇储备再次上升。他们的银行甚至开始向其他国家借出大量外汇:外汇实在是太多了。
中国为什么要减少外汇储备呢?因为对于中国来说,过多的外汇储备已经没有必要了。
1. The credit of RMB has been greatly improved, and the importance of foreign exchange has declined.
After 30 years of development, China has grown into the world's largest industrial producer. They make almost everything. This means that RMB is backed by collateral. When you hold RMB for any country or individual, it means that you can definitely buy the goods you want. This makes many countries happy to accept RMB. Now Middle Eastern countries, Russia and South American countries are willing to accept RMB when selling energy, grain, and minerals to China. The demand for the international currency (the U.S. dollar) has dropped significantly. In 2023, among all international transactions in China, RMB transactions will reach 47%, surpassing the US dollar (45%).
2. Foreign exchange risks are getting higher and higher
Because it reserves too much foreign exchange, China must bear the huge risk of foreign exchange: currency depreciation.
China has more than 3 trillion US dollars in foreign exchange reserves, which means that a 1% duation is worth 30 billion US dollars, which is already more than the annual GDP of many small countries.
In particular, 60% of China's foreign exchange reserves are in U.S. dollars. Against the background of intensified confrontation between China and the United States, risks are getting higher and higher.
Therefore, under normal circumstances, the more foreign exchange reserves, the better When a country's currency is strong enough, its demand for foreign exchange will be greatly reduced. China has entered this stage. In the foreseeable future, China's foreign exchange reserves will continue to decrease.
1、人民币信用大幅提升,外汇重要性下降。
中国经过30年的发展,已经成长为世界最大的工业生产国,几乎所有的东西都是他们制造的。这意味着人民币是有担保的,当任何国家或个人持有人民币时,就意味着你一定可以买到你想要的商品。这使得许多国家乐于接受人民币。现在中东国家、俄罗斯和南美国家在向中国出售能源、粮食和矿产时,都愿意接受人民币。对国际货币(美元)的需求大幅下降。2023年,在中国所有的国际交易中,人民币交易达到47%,超过美元(45%)。
2. 外汇风险越来越高
由于储备了过多的外汇,中国必须承担巨大的外汇风险:货币贬值。
中国有3万多亿美元的外汇储备,意味着每贬值1%就是300亿美元,这已经超过很多小国一年的GDP了。
尤其是中国外汇储备的60%都是美元,在中美对抗加剧的背景下,风险越来越高。
所以,一般情况下,外汇储备越多越好,当一个国家的货币足够强势时,其对外汇的需求就会大大减少,中国就进入了这个阶段,在可预见的未来,中国的外汇储备还会继续减少。
After 30 years of development, China has grown into the world's largest industrial producer. They make almost everything. This means that RMB is backed by collateral. When you hold RMB for any country or individual, it means that you can definitely buy the goods you want. This makes many countries happy to accept RMB. Now Middle Eastern countries, Russia and South American countries are willing to accept RMB when selling energy, grain, and minerals to China. The demand for the international currency (the U.S. dollar) has dropped significantly. In 2023, among all international transactions in China, RMB transactions will reach 47%, surpassing the US dollar (45%).
2. Foreign exchange risks are getting higher and higher
Because it reserves too much foreign exchange, China must bear the huge risk of foreign exchange: currency depreciation.
China has more than 3 trillion US dollars in foreign exchange reserves, which means that a 1% duation is worth 30 billion US dollars, which is already more than the annual GDP of many small countries.
In particular, 60% of China's foreign exchange reserves are in U.S. dollars. Against the background of intensified confrontation between China and the United States, risks are getting higher and higher.
Therefore, under normal circumstances, the more foreign exchange reserves, the better When a country's currency is strong enough, its demand for foreign exchange will be greatly reduced. China has entered this stage. In the foreseeable future, China's foreign exchange reserves will continue to decrease.
1、人民币信用大幅提升,外汇重要性下降。
中国经过30年的发展,已经成长为世界最大的工业生产国,几乎所有的东西都是他们制造的。这意味着人民币是有担保的,当任何国家或个人持有人民币时,就意味着你一定可以买到你想要的商品。这使得许多国家乐于接受人民币。现在中东国家、俄罗斯和南美国家在向中国出售能源、粮食和矿产时,都愿意接受人民币。对国际货币(美元)的需求大幅下降。2023年,在中国所有的国际交易中,人民币交易达到47%,超过美元(45%)。
2. 外汇风险越来越高
由于储备了过多的外汇,中国必须承担巨大的外汇风险:货币贬值。
中国有3万多亿美元的外汇储备,意味着每贬值1%就是300亿美元,这已经超过很多小国一年的GDP了。
尤其是中国外汇储备的60%都是美元,在中美对抗加剧的背景下,风险越来越高。
所以,一般情况下,外汇储备越多越好,当一个国家的货币足够强势时,其对外汇的需求就会大大减少,中国就进入了这个阶段,在可预见的未来,中国的外汇储备还会继续减少。
评论翻译
很赞 ( 17 )
收藏
Surely China does not have all its foreign reserve in us$. Highly likely it is a mix of other major currencies …
中国的外汇储备肯定不全部是美元。很可能是其他主要货币的混合物...
I want to know what’s the foreign reserve for US? If US does not need then that’s China future path. As you can see US and China economies are near parity, and if 2 countries decoupled then there’ll be 2 giant economies, and if all are dealing with one international currency then what’s the reserved currency? It needs time but it’s heading that way.
我想知道美国的外汇储备是多少?如果美国不需要的话,那么这就是中国未来的路径。正如你所看到的,美国和中国的经济实力几乎相当,如果两国脱钩,那么将会有两个巨大的经济体,如果所有国家都使用同一国际货币,那么什么是储备货币?这需要时间,但趋势是这样的。
The United States' foreign exchange reserves are 36.9 billion US dollars (mostly in euros, yen, renminbi, and pounds).
美国的外汇储备为3690亿美元(主要是欧元、日元、人民币和英镑)。
USA spend more money on import than money they make from export, so, most countries and individuals in the world have USD with them. US foreign reserves is the printing machine.
美国的进口支出超过出口收入,因此,世界上大多数国家和个人手中都持有美元。美国的外汇储备就是印钞机。
Not only are China's US Dollar reserves decreasing, but their holdings of US treasury bonds have also reached an all-time low of $769 billion in October 2023, down from $877 billion the previous year.
中国的美元储备不仅在减少,而且他们持有的美国国债也在2023年10月达到了7690亿美元的历史最低水平,比前一年的8770亿美元低。
Taiwan and Hongkong are partially China that means means 4 trillion dollar for China alone
台湾和香港部分属于中国,这意味着中国就有4万亿美元。
I don't see Singapore there. If you have the figures, Singapore would probably be number three in the lineup..
我没有看到新加坡。如果你有数据,新加坡可能会成为排行榜上的第三名。
China our neighbour country has more foreign exchange reserves than any other country in the world. It has got 3.46 Trillion US dollars of foreign exchange if all currencies.
India has only about 550 billion dollars.
我们的邻国中国拥有世界上最多的外汇储备。如果算上所有货币,中国拥有3.46万亿美元的外汇。而印度只有约5500亿美元。
原创翻译:龙腾网 https://www.ltaaa.cn 转载请注明出处
cn has consistently held the largest foreign exchange reserves in the world. the benefits r currency stability, import n export support, debt servicing, investment opportunities, n crisis management.
中国一直拥有世界上最大的外汇储备。其好处包括货币稳定、进出口支持、债务偿还、投资机会和危机管理。
As of today, January 18, 2024, China has a significantly higher amount of foreign exchange reserves than India.
China: The People's Republic of China boasts the highest foreign exchange reserves in the world, clocking in at approximately US$3.24 trillion as of December 2023.
India: India ranks 4th globally with total foreign exchange reserves of around US$586 billion as of September 2023.
Benefits of large foreign exchange reserves:
截至今天,2024年1月18日,中国的外汇储备数量明显高于印度。
中国:中国人民共和国以其约3.24万亿美元的外汇储备量成为全球最高的国家,截至2023年12月。
印度:印度在全球范围内排名第四,截至2023年9月,其外汇储备总额约为5860亿美元。
大规模外汇储备的好处:
Import financing: Foreign exchange reserves can be used to finance imports, especially essential goods like oil and energy. This can be crucial for countries with limited domestic production of these resources.
Investor confidence: Large reserves can signal financial stability and attract foreign investment, which can boost economic growth.
Debt repayment: Adequate reserves can help governments repay foreign debt and prevent potential defaults.
However, there are also potential drawbacks:
稳定性:较大的储备量可以对抗突如其来的外部冲击,如金融危机或货币波动。它们可以帮助一个国家稳定其汇率,并保护其经济免受外部不平衡的影响。
进口融资:外汇储备可以用于进口融资,特别是对于像石油和能源等必需品的进口。对于那些国内生产这些资源有限的国家来说,这可能至关重要。
投资者信心:大规模储备可以显示出金融稳定性,吸引外国投资,促进经济增长。
债务偿还:充足的储备可以帮助政府偿还外债,并防止潜在的违约风险。
然而,也存在潜在的缺点:
Sterilization costs: Central banks may need to engage in sterilization measures like raising interest rates to offset the inflationary impact of reserve accumulation. This can limit economic activity.
Exchange rate manipulation: Some worry that countries with large reserves may artificially manipulate their exchange rates, impacting global trade dynamics.
Ultimately, the optimal level of foreign exchange reserves depends on various factors, like a country's economic structure, trade openness, and vulnerability to external shocks. China and India represent contrasting approaches, with China prioritizing a larger buffer while India focuses on a more manageable level.
I hope this clarifies the situation and provides some insights into the complex world of foreign exchange reserves!
机会成本:持有大量储备意味着在潜在收益较高的投资中持有较少的资产。这可能会放弃潜在的回报,并妨碍经济增长。
对冲成本:央行可能需要采取对冲措施,如提高利率以抵消储备积累的通货膨胀影响。这可能会限制经济活动。
汇率操纵:一些人担心拥有大量储备的国家可能会人为操纵汇率,影响全球贸易动态。
最终,外汇储备的最佳水平取决于各种因素,如一个国家的经济结构、贸易开放程度和对外部冲击的脆弱程度。中国和印度代表了不同的方法,中国优先考虑较大的缓冲储备,而印度则专注于更可管理的水平。